Home » Articles
Blog

Gradio: web applications in python for AI [part1]
Writing web applications for our machine learning and/or artificial intelligence models can take a lot of time and skills that we do not possess. To streamline and speed up this task we are helped by Gradio, a Python library designed to create web applications with just a few lines of code. Let’s discover its basic functionality with some examples.

AI: the best prompt techniques for leveraging LLMs
Prompt techniques are the basis for the use of LLMs. There are several studies and guidelines for obtaining the best results from these models. Let us analyze some of them to extract the basic principles that will allow us to obtain the desired answers according to our task.
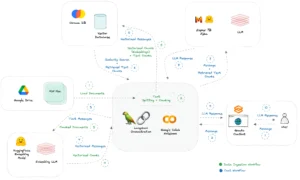
AI: create a chatbot with your own data
ChatGPT allows us to have a virtual assistant at our complete disposal. However, it has one major limitation: it does not know our private data. How can we build our own virtual assistant, or rather a chabot, that uses our data and does not require us to invest money? Let’s find out how to build one using open LLM, free computational environments such as Colab, and Python libraries to manage PDF files and create simple and intuitive web interfaces.

UX/UI design: useful applications
With Figma, the task of designing websites and/or applications has been greatly simplified. In just a few clicks, excellent results can be obtained immediately ready to present to stakeholders and/or developers. However, Figma is not the only tool that can be used! We will find out what other tools can be integrated into the work of designing user interfaces.

UX/UI: Elegance Formula
The definition and development of user interfaces that are attractive, engaging, but above all easy and intuitive is a fundamental step in any application or website. There are a few basic rules that one must consider, although our personal aesthetic and creative taste will then influence our choices. By following the Formula of Elegance, however, fewer mistakes will be made and the final product will be as intuitive and inclusive as possible.

The best Python frontend libraries for data science
Developing web and desktop applications requires knowledge of several programming languages. Defining user interfaces is a fundamental aspect of providing a good user experience (UX) and viewing information in an effective and appealing manner. For those involved in analysing data or collecting it, however, this aspect is critical. In fact, many developers specialise in one language and are reluctant to expand their knowledge to other languages or tasks that are not their core business. For this reason, in this article we present five libraries in python that can facilitate and speed up the development of user interfaces.
